
When we start the car we are not usually aware of the multiple mechanical processes that have to take place for the engine to work. These are given thanks to the communion and joint work of countless pieces and moving parts that work in a synchronized way. One of these elements is engine valves because without them it would not be possible to obtain the necessary energy from an engine.
What are the valves of an engine?
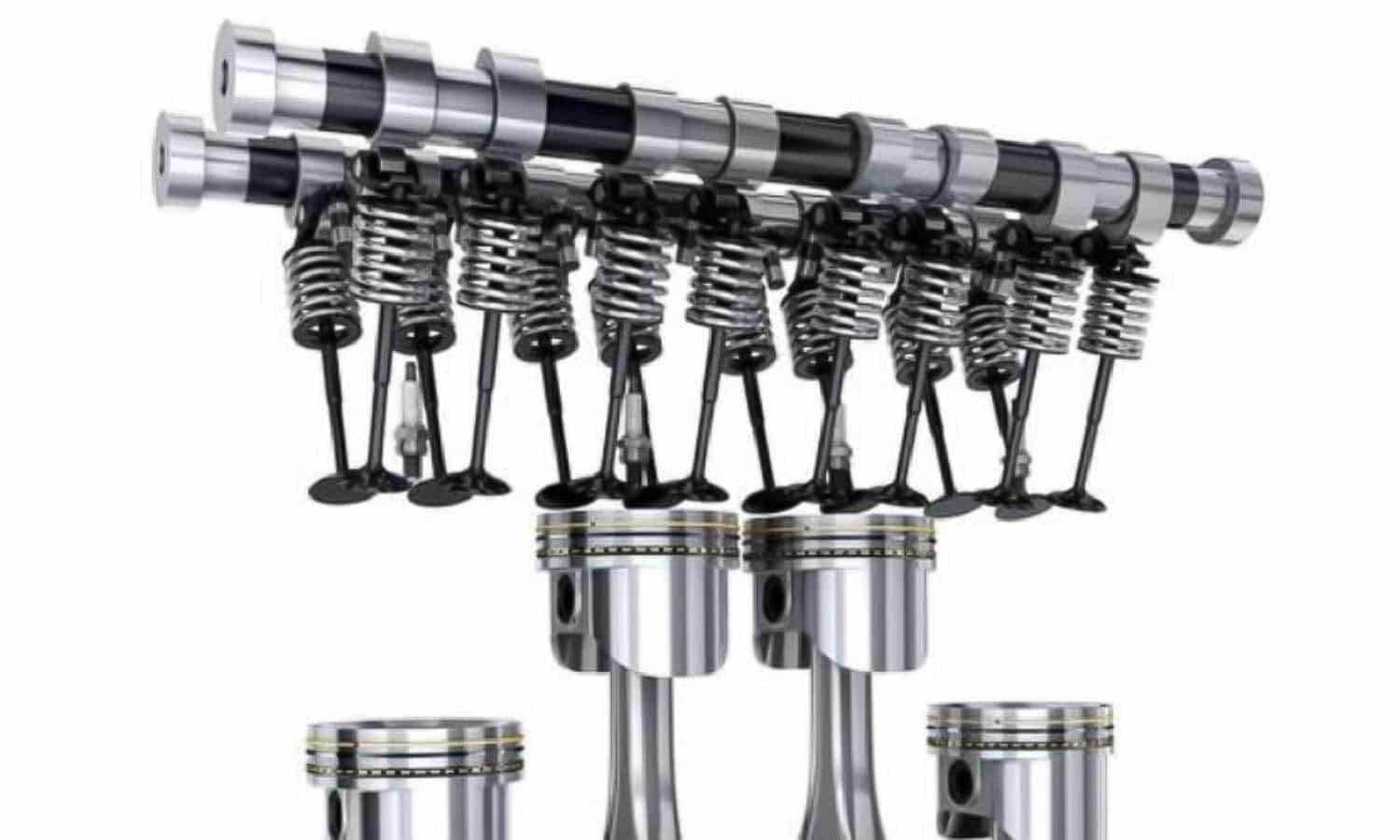

The valves of an engine are the metal elements that allow entry to the combustion chambers of the fuel-air mixture and the exit from it of the gases produced by its explosion. Without these mechanical elements, the operation of the motor would be unfeasible as its movement is vital for the energy necessary to move the wheels to be produced.
Structurally, a valve is made up of a long part called the spigot or tail of the valve (commonly stem) and another upper part called head (plate or valve head). For its manufacture, alloyed materials are used as they must withstand high temperatures in their operating cycle (up to 1000º centigrade).
What is the actual function of the valves in an engine?
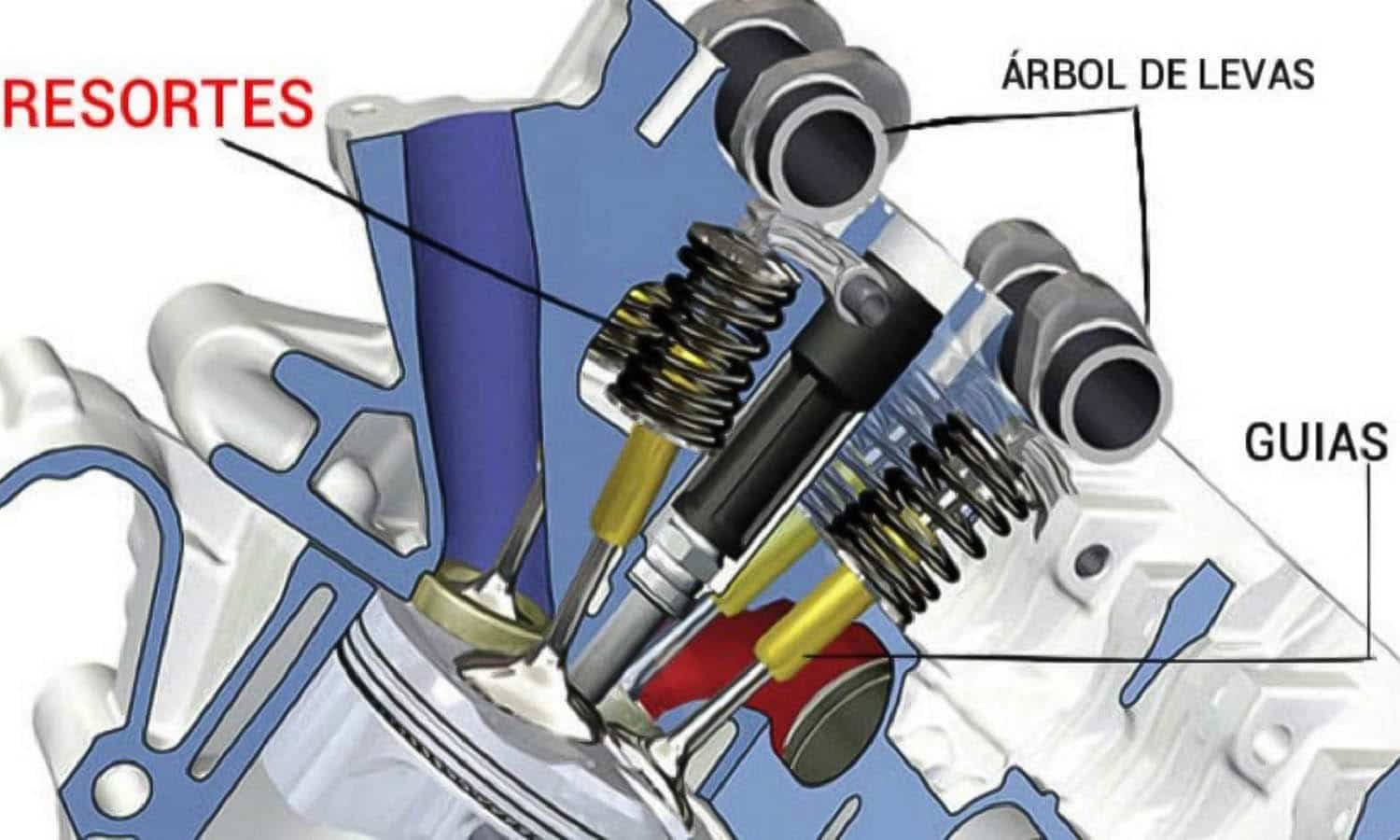
The actual function is very basic and simple. They are in charge of manage fuel and air intake (fuel-air mixture) to the cylinder. After the explosion of the mixture by the piston compression They are the ones that allow the exit of the gases resulting from this explosion.
Where in the engine are the valves located?
Technically are located on the cylinder head (commonly known as butt). The wide part (valve head) rests on the cap fitting perfectly to properly seal the cylinder. The lower part or rod is located inside the guide, limiting itself to completing the opening and closing movement ordered by the camshaft and the springs.
Are all engine valves the same?
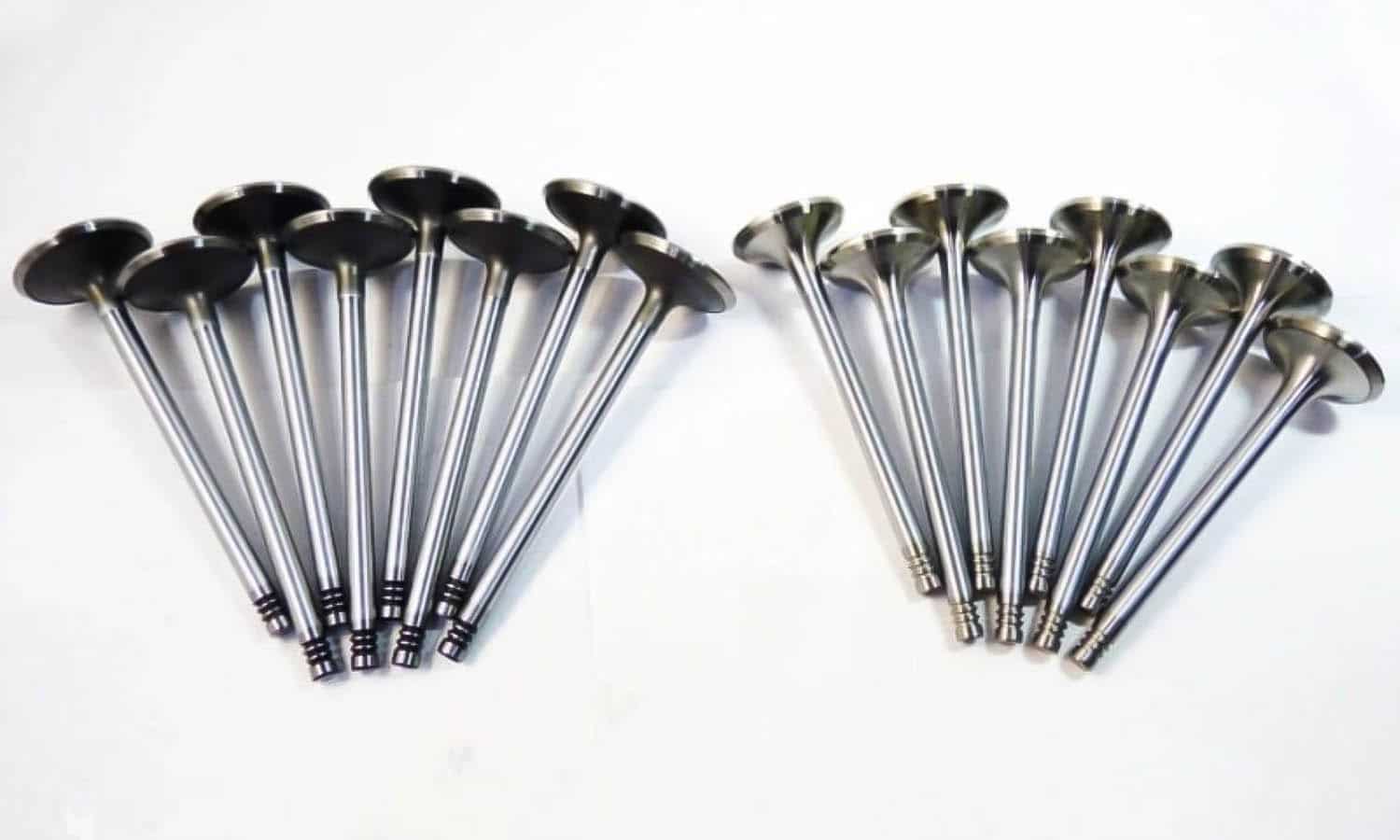

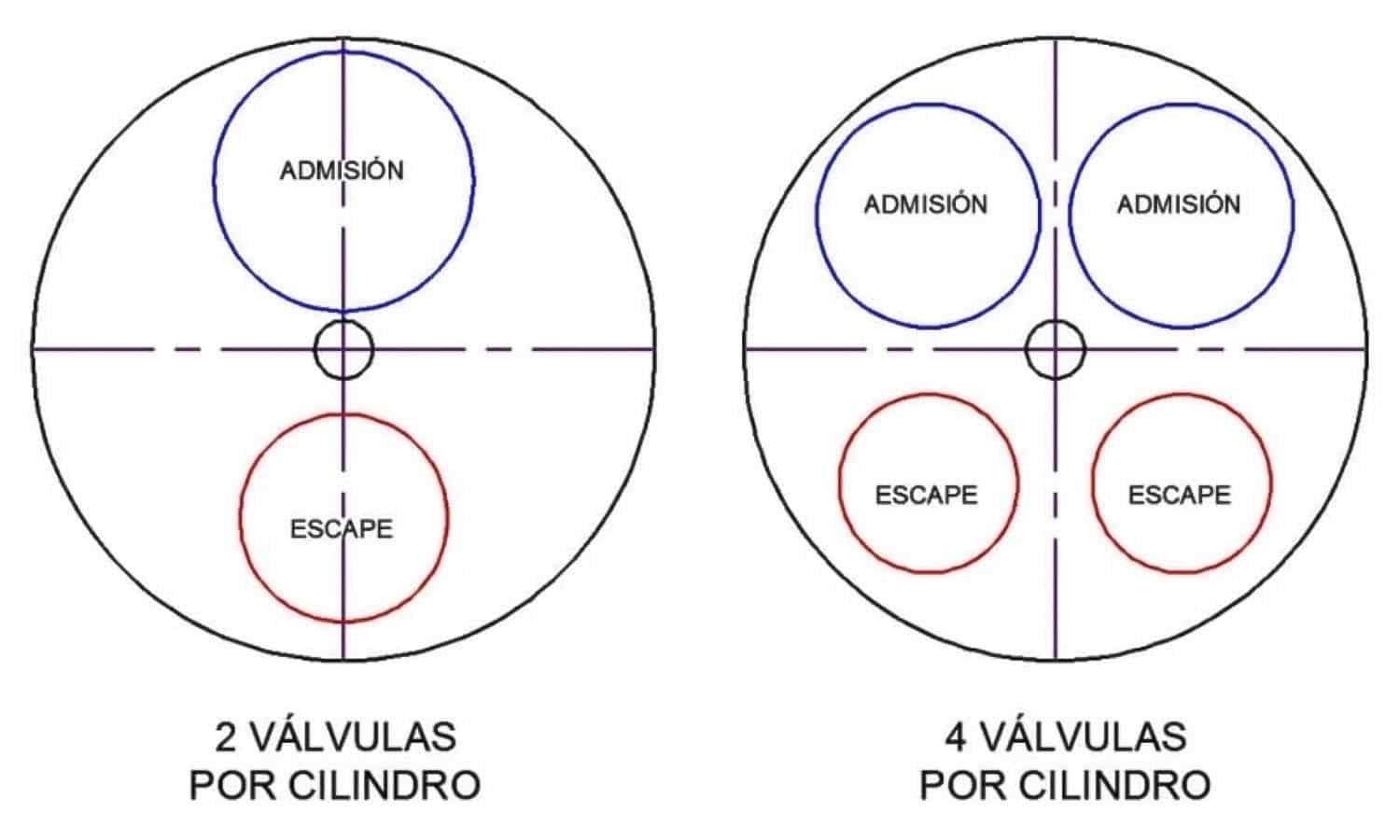
No, the answer is no. The intake valve (where the mixture enters) is larger than the exhaust valve (where the gases exit). The reason for this different size is due to the conditions in which the intake and exhaust occur. The pressure at which the mixture enters is similar to that which exists in the atmosphere, so in order to favor the process, its size is larger.
On the contrary, when the mixture has already exploded, the gases are at a higher pressure, so it is not necessary for their size to be so large. In addition, also there is a difference in the materials with which they are manufactured. The intake valve withstands about 200º centigrade and the exhaust valve about 700º centigrade, so its components are more resistant than those of the first.
Finally, to correctly distinguish one type of valve from the other we only have to look at the size of your head and its shape. We know that the intake ones have a larger head but it is also flat on the front side, however the exhaust ones, in addition to having a smaller head, have a more conical shape on the front side.

What happens if a valve is damaged?

If a valve breaks down, the first thing that will happen is that the explosion or expulsion of gases will not take place correctly. This is due to the fact that by not resting the valve well on the engine cover, the gases will leak and therefore a compression and thermal imbalance will occur, causing a major breakdown.
The main problem that the valves have to deal with is their little or no cooling, because if the engine is well lubricated there is no risk of failure. Solving a fault of this type has a variable cost, since it will depend on how they have failed and the damage that has occurred in the engine. The unit cost of a valve is very low, since its manufacture is cheap, however, the final figure will vary depending on the type of valve and the problem detected.

Ultimately
Valves are elements that have the simple function of closing and opening the intake and exhaust ducts of gases, having main function in the combustion of the air-fuel mixture.
Currently, the most widely accepted valves are the so-called «plate», due to their inverted plate shape in its vital part, that is, the one that opens and closes the ducts.
From the center of the same begins what is called "spike", a cylindrical extension that moves the valve, although the «informal» denomination of calling Head to the valve plate, and Glue to the spike
They are manufactured cast and machined in special steels, because what is sought is withstand high temperatures that the gases reach during their operation.

Differences between exhaust and intake valves
All the heat differences between exhaust and intake allow the use of special alloys in the exhaust valves (which withstand the 1000 degrees centigrade)
In addition to being quite inexpensive to manufacture, these valves allow little walking area, less friction and an appropriate shape for the correct gas flow.
The only drawback they have is the little or no cooling what are they presenting.
Images – Henri Bergius, Mirko Junge, lw5315us
Thanks for the information
What happens if the intake valve of a motorcycle resumes a little gasoline?
Excellent contribution, thanks.