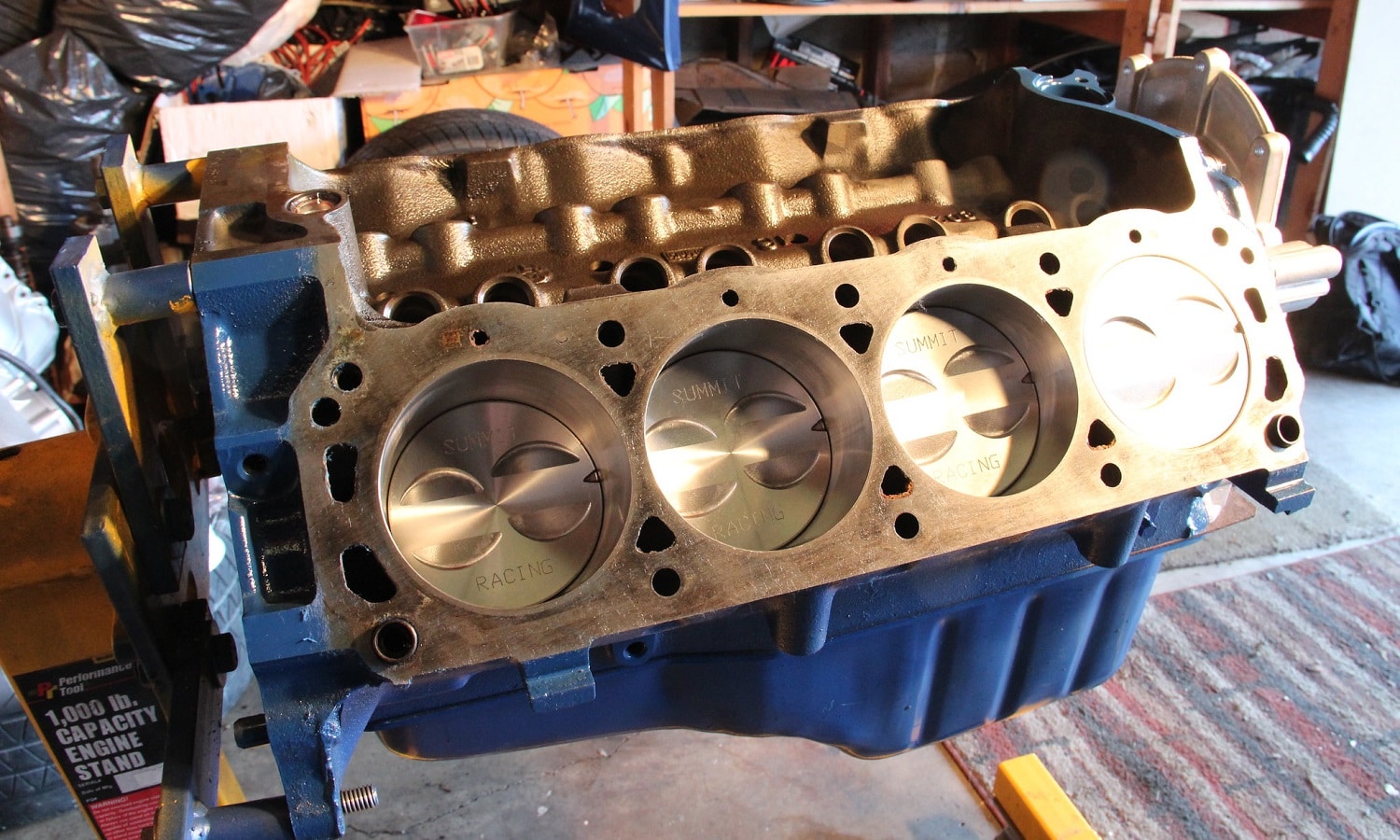

The displacement of an engine is obtained by performing mathematical calculations that derive from the geometric measurement of its components. Specifically, the part of the engine that generates the driving force. Nevertheless, do not confuse the unit cylinder capacity with the total, since they refer to different values.
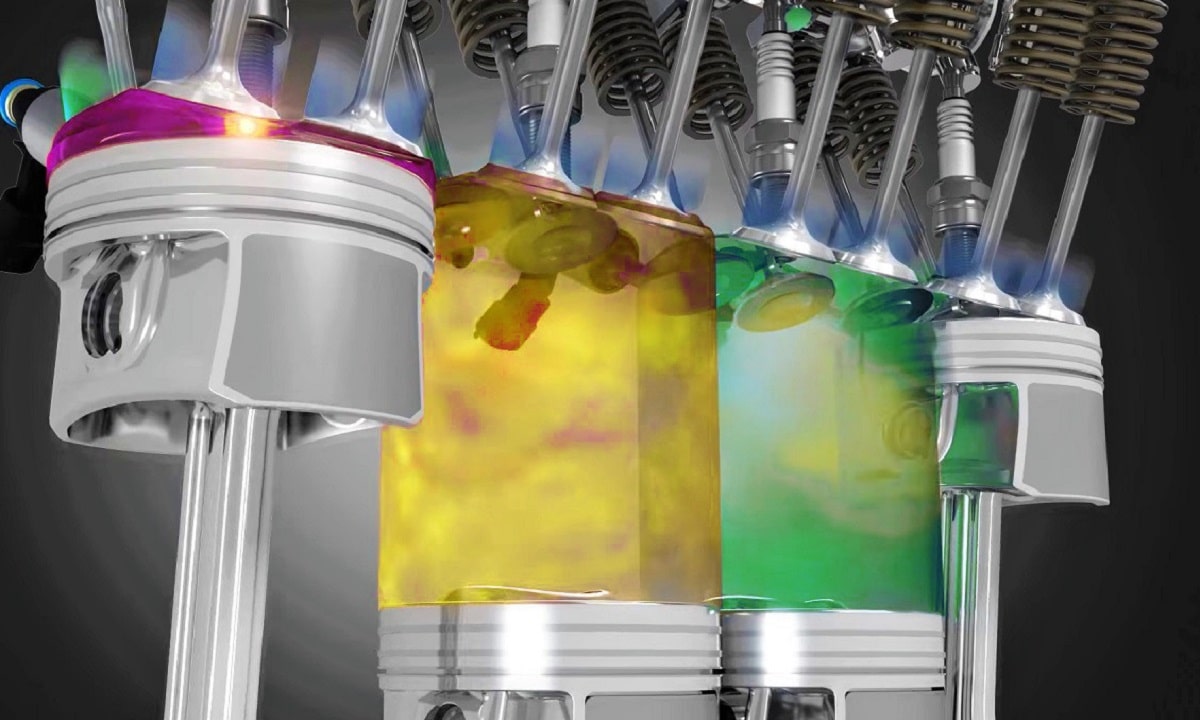
Although many people believe so, the displacement of an engine it is not all the gap inside the cylinders. It's just about space used to create movement of the pistons. That is, the volume between the Top Dead Center and the Bottom Dead Center of the pistons.
Everything else, is out of what is considered engine displacement. What e.g., combustion chambers, which are a space where the explosions start, but where the piston does not rise. Nor do they count, of course, the parts of the cylinders to which the heads of the pistons do not go down.
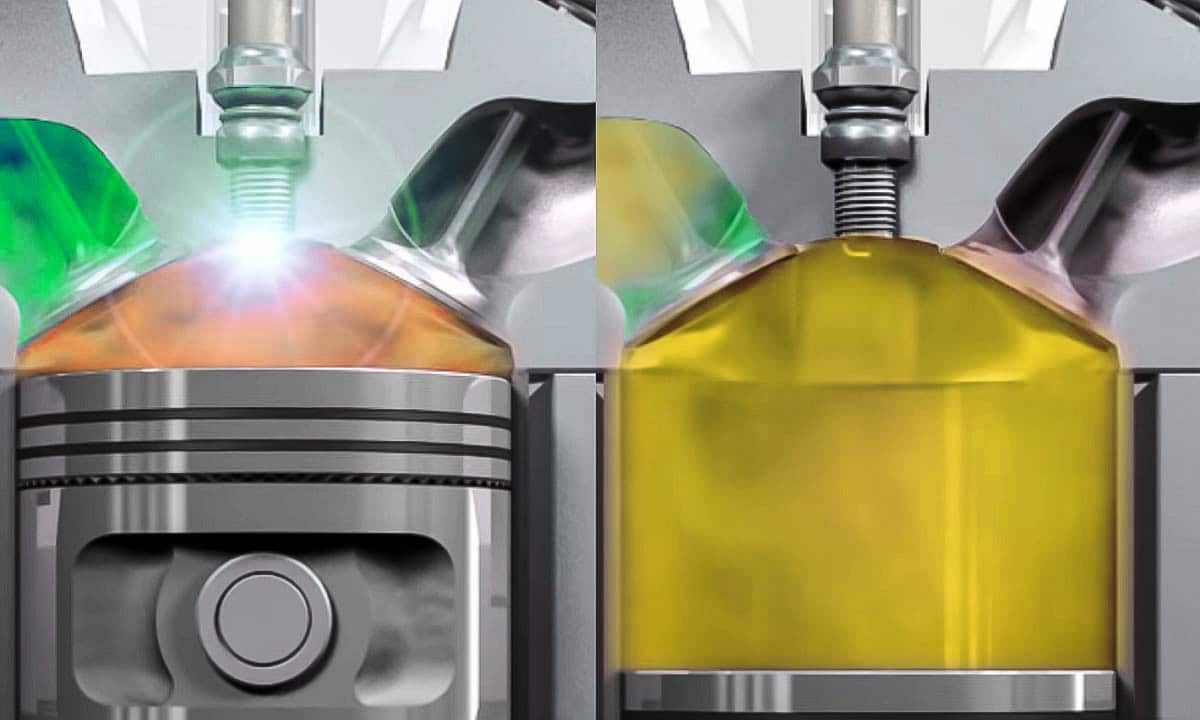

unit displacement
It is the volume of only one of the cylinders the motor. As we have told you, it is about measuring the space between the Top Dead Center and the Bottom Dead Center of the piston. Which is obtained with the following formula: π x (cylinder diameter²/4) and multiplying it by the height of the total travel or Piston race.

Of course, in the engines of variable compression, taking into account the compression ratio highest. That is, when the engine is running with the largest possible piston stroke. If you do not know this type of motors, we recommend that you take a look at the article compression ratio of an engine. At the end it has a section that explains its advantages and how it works.
Total displacement
In this case, we are already talking about the displacement of an engine, which is what is usually advertised in the different vehicles that are for sale. The total displacement is simply the result of multiply the value obtained with the calculation of the unit displacement, by the number of pistons with which the engine has.

Notice that it is the number of pistons, not the number of cylinders. Although it is not common to see them, an incorrect value would be obtained in opposed piston engines, because they have two pistons per cylinder. A feature that can be seen for example in the INNEngine motor. In any case, it is indifferent to use cylinders or pistons in the rest of the engines.
Each result obtained in these calculations, and since the diameter of the piston is usually expressed in millimeters, it will be expressed in cubic millimeters. Therefore, to obtain the displacement in cubic centimeters (as it is often expressed) we must divide the result by 1000.
What is unit and total cylinder capacity used for?
Apart from the use of these values in the world of engine engineeringDe of modification y reparación, is also used, for example, in the calculation of the fiscal horses of a vehicle with heat engine. In the formulas used for this, measurements such as the diameter of the cylinders and the stroke of the pistons appear.
Going back to engine engineering, unit, total cylinder capacity and the relationship between them is commonly used. For example, for conventional motors it is that the relationship between the two is neither too big nor too small. In other words, do not fall into cylinders that are too small for the displacement of the engine or the opposite.
Low unit displacement (small cylinders)
Too small cylinders cause, for example, that the amount of mixture is less and therefore that the generated torque is less. What can be solved with supercharging, although with certain limits that are not exceeded in conventional cars that we generally see on the street.
High unit displacement (large cylinders)
It should not be forgotten that gasoline ignition is not instantaneous and the flame it generates takes time to expand. The larger the cylinder, the longer it will take to push the piston effectively, because it will take time to arrive. Which can be fixed to a certain extent with further ignition advance. However, this advancement has limits and cannot be abused.
The result is that engine revs can't be too high, because the flame does not have time to move the motor at certain turning speeds. Also, the bigger the cylinder, the higher the speed the piston has to reach to cover the entire movement and, again, that generates more friction and heat.
The advantage is that a large cylinder allows older Válvulas for the entry of air or mixture and the expulsion of gases. In addition to making it easier to incorporate systems of two plugs.

As you can see, both cases bring extra problems what needs to be solved. For that reason, in addition to others, it is why you see more and more engines with a very low total displacement, but three cylinders. For example, in the 0,9 liter, 1.0 liter or even 1.2 liter engines. Despite the extra vibrations they cause, mainly at low revs.
Can the displacement be changed?
Although the motor power-ups most frequent only involve a reprogramming of the electronics, there are also modifications deeper that even manage to modify the unit displacement and, logically, the total. A good example of this is the Brabus 900 G65. A modification of the 2016 Mercedes G-Class with a 12-liter 6.0-cylinder engine, which after the changes had a volume of 6.3 liters.

As you have seen, we have mentioned both the diameter of the cylinders and the piston stroke. Both values are subject to change by a preparer. For example, the diameter is usually enlarged through precision grinding machine, which decreases the thickness of the cylinder walls. A resource from which do not abuse due to the strength limits of the engine block. What will you have to put up with? the same load, friction and heat with a thinner wall. This of course supposes an increase in the size of the pistons in the same measure.
With regards to Piston race, can also be modified, although that may lead to changes in Rods, crankshaft and other related items. Also, can't be abused either of this modification since the piston speed will increase at each revolution of the motor and that increases the heat due to friction, in addition to other problems.
Image 1 – Nick Ares ; Picture 5 – Eric Kilby
Very interesting and at the same time very easy to understand, I don't know if it can provide exercises related to cylinder capacity.
Hello, can someone tell me this exercise please! A car has a four-cylinder engine. The diameter of each cylinder is 83mm and the piston stroke is 90mm.
489 cm3 unit cylinder and for 4 gives 1947,8 cm3 or 1,947 lt.
I need to calculate the cylinder capacity of four engines but I don't know where to get the calculations from, please can you help me with four kinds of engines and their data
engine type and year please
This topic is very interesting and easy to understand what they teach us.
the base of the piston can also be calculated (easier in my opinion) by doing Π X Radius of the piston squared and then multiplied by the stroke to give the unit displacement
You can develop this exercise with all the steps a 6-cylinder engine has a diameter of 80mm and a stroke of 70mm calculate the unit displacement and the total thanks
Diameter 8'0 cc
Stroke 7'0cc
We multiply the diameter by itself, the result is multiplied by the number pi which is 3'1416, which we divide by 4, and multiply by the stroke and it gives us the volume per cylinder, then it is multiplied by the number of cylinders and we have the total.
8'0 X 8'0 X 3'1416
————————- =50'265 X 7'0 =351'85 Volume of a cylinder
4
351'85 X 6 cylinders = 2.111'15 total displacement.
thanks you cleared my doubt with this example (Y)
could you support me to know about cubis centimeter stories is a suburbn 2014 best regards
Hello, I am a third-year student of this and I would like if you asked me to advise some type of exercise to practice calculating the displacement of an engine.
No we can't thunder xD
can carry out this exercise: of a 6-cylinder engine with a piston diameter of 82.7 mm and a stroke of 83.5 mm, using at least two decimals in the operations, calculate the total displacement in cubic centimeters and in liters, as well as what is the compression ratio knowing that the volume of the compression stroke is 49.82.
Thanks for the contribution of the good understanding on concepts and easy to understand examples,